 |
ElmerFoamFSI
2.0
ElmerFoamFSI is fluid-solid interaction simulation application built up from OpenFOAM CFD and Elmer CSM coupled through the IMPACT multiphysics software integration infrastructure.
|
 |
ElmerFoamFSI
2.0
ElmerFoamFSI is fluid-solid interaction simulation application built up from OpenFOAM CFD and Elmer CSM coupled through the IMPACT multiphysics software integration infrastructure.
|
The simple dynamic problem tests the accuracy of the ElmerFoamFSI suite. Here we have a viscous fluid (  ) subjected to a velocity profile to generate a simple, in-plane traction to the walls of a channel.
) subjected to a velocity profile to generate a simple, in-plane traction to the walls of a channel.
One of these walls is a cantilever beam (  ) ; friction-based traction is applied to the top face of the cantilever to create axial deformation (
) ; friction-based traction is applied to the top face of the cantilever to create axial deformation (  ) .
) .
The boundary conditions are motivated by axial deflection on the beam, therefore, the effect of the vertical deflection created by potential mornal pressure is negligible.
Figure 1 below shows the geometry of the problem.
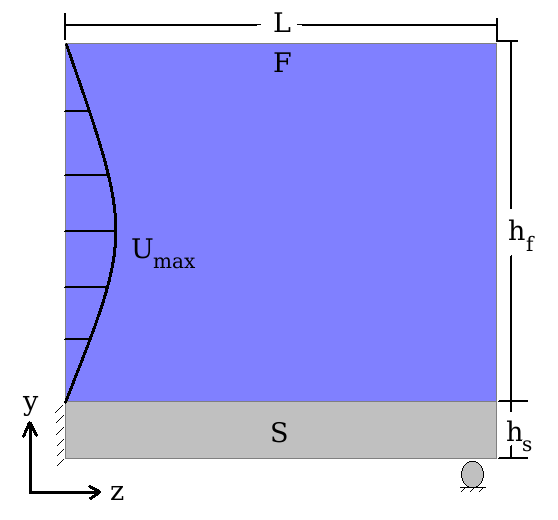
The dimensions of the domain are 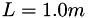 ,
, 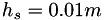 , and
, and 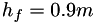 . The velocity profile is symmetric with
. The velocity profile is symmetric with 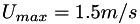 and axis of symmetry at
and axis of symmetry at 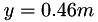 .
.
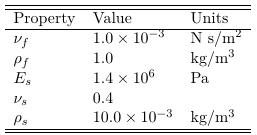
The out-of-plane dimension is selected to be 0.1 m for both domains, arbitrarily. The table below summarizes the properties of the solid and fluid used in the simulation.
The velocity profile is ramped from zeros to its final form with transition period of 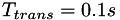 and then kept constant for the rest of simulation. The total simulation time is selected to be
and then kept constant for the rest of simulation. The total simulation time is selected to be 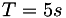 .
.
In ElmerFoamFSI, OpenFOAM (a finite-volume solver) is used as the fluid solver and Elmer (a finite-element solver) is used as the structural solver.
Here both weak and strong coupling approaches can be used to solve FSI problems. The simple dynamic problem currently utilizes a weak-coupling algorithm.
Please take a look at Setting up Example Problems for further information regarding the structure of each input file.
Elmer can be used to find deformation of a solid object, ( 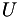 ), subjected to different types of loads.
), subjected to different types of loads.
To capture large deformations in the solid, ElmerFoamFSI uses the non-linear solver. Here the description of the problem starts with the input files:
The .GRD file provides the description of the geometry of the problem.
The .SIF file provides rest of the definitions, including material properties and boundary conditions.
Here, OpenFOAM acts as the fluid solver to solve for the fluid pressure ( 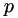 ) and velocity (
) and velocity (  ) found in ./fluid/0/ .
) found in ./fluid/0/ .
To capture deformations of the solid/fluid interface, OpenFOAM performs mesh update and re-meshing procedures to maintain the quality of the grid.
OpenFOAM requires both definition of the solid and the fluid sections of the grid; in ElmerFoamFSI, the solid definition is replaced by Elmer.
To setup a fluid problem, a strict folder/file hierarchy must be followed, as described below.
There should be at-least three major sub-folders in the main fluid problem (./fluid/ ):
These sub-folders are:
The requirements listed in this dynamic example are an extension of the instructions given in main and should be completed before starting the following steps.
In order to execute the simple dynamic verification problem with ElmerFoamFSI and Elmer input, an ElmerFoamFSI input file should be copied to the ./fluid. folder of the OpenFOAM input hierachy. The following directions are the steps to run a problem :
Make sure your folder has following files: Allclean, Allrun, AllrunPar, makeLinks, makeSerialLinks, removeSerialLinks (scripts so far), fluid(folder), solid(folder)
./path/to/elmerfoamfsi/elmerfoamfsi test.config (typically found in the top level /build/bin folder)
As a result of simulation, you will obtain VTK,VTU outputs along with many log files. Output files can be further post processed by using tools such as Paraview.